
When managing your website’s DNS settings, understanding the terms “DNS Zone” and “DNS Domain” is crucial. Many website owners and administrators often ask, “What is a DNS Zone?” and “What is a DNS Domain?” These concepts play vital roles in how your domain name translates to an IP address and how your website is managed online. In this guide, we will demystify these terms, showing their differences and why they matter, especially for users of No-IP.
DNS Domain
What is a DNS Domain?
A DNS Domain is the unique name that identifies a website or resource on the internet. It’s what people type into their browsers to visit your site, like `example.com`. Here’s a breakdown of its structure:
Structure of a DNS Domain
- Root Domain: The top-most level of the domain name system, often represented by a dot (`.`).
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): The extension that follows the root domain, such as `.com`, `.org`, or `.net`.
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the primary name chosen by the domain owner, such as `example` in `example.com`.
- Subdomains: Prefixes added to the domain to create additional website sections, like `blog.example.com` or `shop.example.com`.
Function of a DNS Domain
A DNS Domain serves as a human-readable address for accessing online resources. When a user enters a domain name in their browser, the DNS system translates it into an IP address, which directs the browser to the appropriate server hosting the website. For instance, typing `no-ip.com` resolves to the IP address where No-IP’s services are hosted.
DNS Zone
What is a DNS Zone?
A DNS Zone is a distinct part of the DNS namespace that an administrator or organization manages. It includes the DNS records that dictate how your domain is resolved and configured.
Structure of a DNS Zone
- Primary Zone: Contains the authoritative DNS records for a domain.
- Secondary Zone: A backup copy of the primary zone, used for redundancy.
- Zone File: A text file with DNS records, including:
- A Record: Links a domain to an IP address.
- CNAME Record: Aliases one domain name to another.
- MX Record: Specifies the mail servers for a domain.
- TXT Record: Holds text information for various uses, such as email validation.
Function of a DNS Zone
A DNS Zone allows you to manage how your DNS Domain is resolved on the internet. It defines the mappings between your domain and its corresponding IP addresses, subdomains, and other DNS settings. This management is essential for ensuring that users can reach your site and that services like email function correctly.
Key Differences Between DNS Zones and DNS Domains
Understanding the differences between a DNS Zone and a DNS Domain is essential for effective DNS management:
- Scope: A DNS Domain is the unique name used to identify resources, while a DNS Zone is the area where DNS settings are administered.
- Management: DNS Domains are the addresses you register and use, while DNS Zones contain the configuration records for these addresses.
- Configuration: DNS Zones include detailed settings for resolving domain names, while DNS Domains are the user-facing names.
Real-World Examples of DNS Zones and Domains
- DNS Domain Example: Typing noip.com into your browser is how users reach No-IP’s services.
- DNS Zone Example: Behind the scenes, the DNS Zone for noip.com contains records like the CNAME that control where the domain points and how email is routed.
Visual Comparison
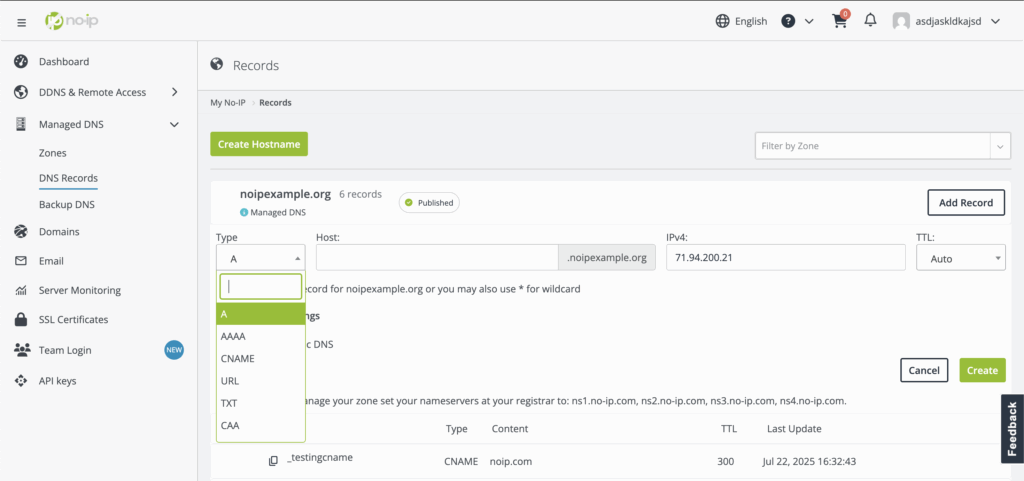
Why This Knowledge is Important
Understanding the difference between a DNS Zone and a DNS Domain is crucial for:
- Efficient DNS Management: Properly configuring your DNS Zone ensures your DNS Domain is accessible and reliable.
- Troubleshooting: Knowing whether issues are related to DNS Zone configurations or DNS Domain settings can speed up problem resolution.
- Advanced Features: Utilizing No-IP’s services effectively, such as dynamic DNS, requires a good grasp of how DNS Zones manage changing IP addresses.
How No-IP Simplifies DNS Management
At No-IP, we make managing DNS Zones and DNS Domains straightforward:
- Dynamic DNS: Automatically update your domain to point to the correct IP address, even if it changes.
- Managed DNS Services: Let No-IP handle the complexities of DNS, ensuring your domain is always reachable.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easily set up and manage your DNS records within your DNS Zone, including subdomains and email settings.
In summary, understanding what a DNS Zone is and what a DNS Domain is helps you manage your online presence more effectively. A DNS Domain is the unique name used to access resources, while a DNS Zone is where you manage the settings for that name. At No-IP, we provide the tools and support to simplify your DNS management, making it easier for you to maintain a reliable and accessible website.
Ready to enhance your DNS management? Explore No-IP’s DNS solutions today and see how we can help you streamline your domain and DNS settings!